function random-mac {
$mac = "02"
while ($mac.length -lt 12)
{
$mac += "{0:X}" -f $(get-random -min 0 -max 16)
}
$Delimiter = "-"
for ($i = 0 ; $i -le 10 ; $i += 2)
{ $newmac += $mac.substring($i,2) + $Delimiter }
$setmac = $newmac.substring(0,$($newmac.length - $Delimiter.length))
$setmac
}
function disconnect-wifi {
$CurrentSSID = (& netsh wlan show profiles | Select-String 'Current User Profile' | Foreach-Object {$_.ToString()}).replace(" Current User Profile : ","$null")
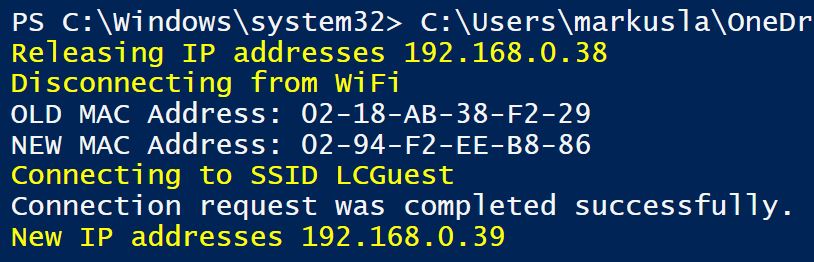
Write-Host "Current WLAN SSID: $CurrentSSID" -ForegroundColor Yellow
$WIFI = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration | Where { $_.IpEnabled -eq $true -and $_.DhcpEnabled -eq $true}
Write-Host "Releasing IP addresses:" ($WIFI.IPAddress | select -first 1) -ForegroundColor Yellow
$WIFI.ReleaseDHCPLease() | out-Null
# Make sure the Release have happened, else it give it 2 sec extra.
$WIFI = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration | Where { $_.IpEnabled -eq $true -and $_.DhcpEnabled -eq $true}
if ($WIFI.DefaultIPGateway -ne $Null) {
Write-Output "Release of IP Address had not completed, waiting 1 Seconds"
sleep -Seconds 2
}
Write-Host "Disconnecting from WiFi" -ForegroundColor Yellow
& netsh wlan disconnect | Out-Null
}
function new-wifimac ($wifiadapter, $ssid, $newmac){
# Write-Output "Wifi AdapterName: $wifiadapter"
# Write-Output "SSID: $ssid"
# Write-Output "New MAC Address to set: $newmac"
$oldmac = (Get-NetAdapter -Name $wifiadapter).MACAddress
Write-Output "OLD MAC Address: $oldmac"
if ($oldmac -like $newmac) {
Write-Host "Old MAC and New MAC are identical, generating a new MAC Address" -ForegroundColor Red
$newmac = random-mac
Write-Output "New MAC Address to set: $newmac"
}
Get-NetAdapter -Name $wifiadapter | Set-NetAdapter -MACAddress $newmac -Confirm:$false
Get-NetAdapter -Name $wifiadapter | Disable-NetAdapter -Confirm:$false
Get-NetAdapter -Name $wifiadapter | Enable-NetAdapter -Confirm:$false
$currentmac = (Get-NetAdapter -Name $wifiadapter).MACAddress
Write-Output "NEW MAC Address: $currentmac"
Write-Host "Connecting to SSID: $ssid" -ForegroundColor Yellow
& netsh wlan connect name=$ssid ssid=$ssid
$NoIP = 0
Do {
$WIFI = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration | Where { $_.IpEnabled -eq $true -and $_.DhcpEnabled -eq $true}
if ($WIFI.DefaultIPGateway -ne $null) {
$NoIP = 5
}
else {
sleep -Seconds 2
Write-Host "Waiting for IP Address"
$NoIP += 1
}
} While ($NoIP -lt 5)
Write-Host "New IP addresses" ($WIFI.IPAddress | select -first 1) -ForegroundColor Yellow
}
function test-wifi ($probe){
if (Test-NetConnection -ComputerName $probe -CommonTCPPort HTTP -InformationLevel Quiet) {
$result = "Working"
}
else {
$result = "NotWorking"
}
$result
}
# Specify $SSID manually
# $ssid = 'SSID-to-Connect-to'
#
# Or use the currently used SSID to reconnect to.
$ssid = (& netsh wlan show interfaces | Select-String ' SSID ' | Foreach-Object {$_.ToString()}).replace(" SSID : ","$null")
# Specify WLAN Adapter Name Manually
# $wifiadapter = 'vEthernet (External Wi-Fi)'
#
# Or Try to identify the Wi-Fi Adapter
$wifiadapter = (Get-NetAdapter | where Status -EQ "Up" | where MediaType -EQ "802.3" | where MacAddress -EQ (Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration | Where { $_.IpEnabled -eq $true -and $_.DhcpEnabled -eq $true} | select *).MACAddress.replace(":","-")).Name
# Specify a MAC Address manually
# $newmac = "02-F4-D7-B2-FE-D8"
#
# Or generate a new Random MAC Address
$newmac = random-mac
disconnect-wifi
new-wifimac -wifiadapter $wifiadapter -ssid $ssid -newmac $newmac
test-wifi -probe www.msftncsi.com